Babylon was the capital of the great Babylonian empire. The ruins of the city, which was founded more than 4,000 years ago as a tiny harbor on the Euphrates River, are located in modern-day Iraq. Under Hammurabi’s control, Babylon grew to be one of the most powerful cities in the ancient world.
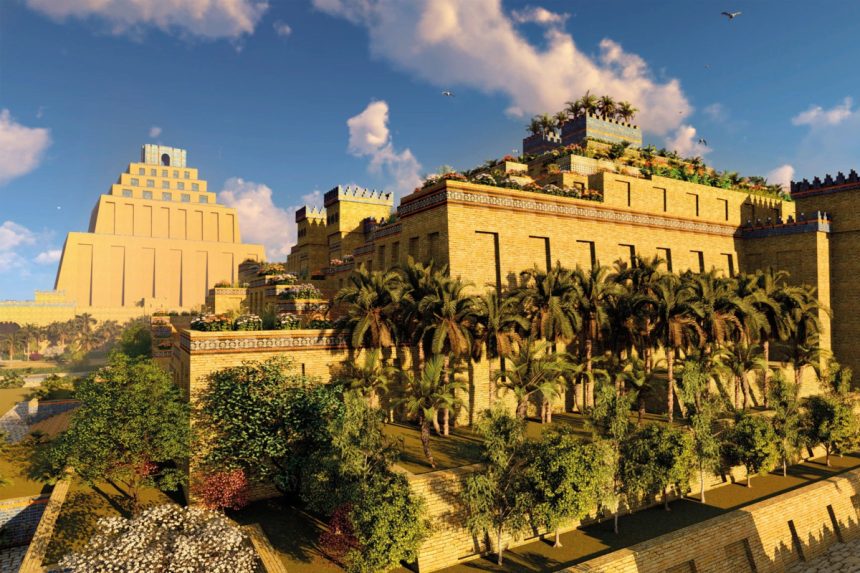
A new dynasty of monarchs formed a Neo-Babylonian Empire that stretched from the Persian Gulf to the Mediterranean Sea centuries later. During this time, Babylon became known for its exquisite architecture, which included the Hanging Garden of Babylon, Ishtar Gate, and the Tower of Babel.
Where exactly is Babylon?
Babylon was about 50 miles south of Baghdad along the Euphrates River in modern-day Iraq. The ancient Akkadian-speaking people of southern Mesopotamia founded it at approximately 2300 B.C.
Under Amorite monarch Hammurabi, who reigned from 1792 to 1750 B.C., Babylon became a prominent military power. After conquering adjacent city-states, Hammurabi consolidated much of southern and central Mesopotamia under Babylonian control, establishing the Babylonian empire.
Hammurabi made Babylon a wealthy, powerful, and influential metropolis. He wrote one of the world’s first and most comprehensive written law codes. It was known as the Hammurabi Code, and it assisted Babylon in defeating other communities in the area.
However, Babylonia was short-lived. After Hammurabi’s death, the empire disintegrated and reverted to a minor kingdom for several centuries.
Empire of Neo-Babylonia
The Neo-Babylonian Empire, which existed from 626 B.C. to 539 B.C., was formed by a new dynasty of kings. After conquering the Assyrians at Nineveh in 612 B.C., the Neo-Babylonian Empire rose to become the world’s most powerful state.
In the Near East, the Neo-Babylonian Empire had a cultural rebirth. During King Nebuchadnezzar II’s reign, the Babylonians erected many gorgeous and extravagant palaces and saved monuments and artworks from the earlier Babylonian Empire.
The Fall of the Babylon Empire
The Neo-Babylonian Empire, like the older Babylonian Empire, was quite short. The legendary Persian monarch Cyrus the Great captured Babylon in 539 B.C., less than a century after its creation. When the empire fell under Persian authority, the fall of Babylon was complete.
Babylon in recent times
The Iraqi government excavated Babylonian remains and sought to rebuild certain parts of the old city, including one of Nebuchadnezzar’s palaces, during Saddam Hussein’s reign.
Following the 2003 invasion of Iraq, US forces established a military base on the ruins of Babylon. According to the United Nations cultural heritage agency UNESCO, the base caused “significant damage” to the ancient site. In 2009, the site reopened to tourists.